Backconnect proxy: Explanation & comparison to other proxies
Scaling up your web scraping project is not an easy task.
Adding proxies is one of the first actions you will need to take. You will need to manage a healthy proxy pool to avoid bans.
There are a lot of proxy services/providers, each having a whole host of different types of proxies.
In this blog post, you are going to learn how backconnect proxies work and when you should use them.
The web scraping proxy landscape
Before we get into the details of backconnect proxies it’s important to understand the different types of proxies. Here’s a summary:
IP address
So, first of all, we can refer to proxies based on the IP address type:
- Datacenter
- Residential
- Mobile
A backconnect proxy network can be a set of any of these or even a combination of these.
Knowing what kind of address you need for your web scraping project is important. You can read more about IP address types in our web scraping proxy guide!
Proxy quality
We can also group proxies together based on their quality:
- Public/open: free proxies
- Shared: multiple users use the same proxy, shared resources
- Dedicated: only accessible to you
Public proxies are free and can be used by anyone. Hence, the quality is poor and you probably can’t use them to scale your web scraping. Dedicated proxies are the best for web scraping. Only you can access them and you have all the control over them.
Proxy management
Finally, we can define proxies based on if they are managed proxies or not:
- Regular proxy: a single proxy that you can use to access a website, not managed
- Backconnect proxy: a managed proxy network (or pool) with features helping you scrape websites
Now let’s see the difference between these two types.
How regular proxies work
The way a regular proxy server works is pretty simple. You send your request through one proxy and hope that you will get a successful response back. If the IP address is banned you will need to try it with another proxy. Here’s an illustration:
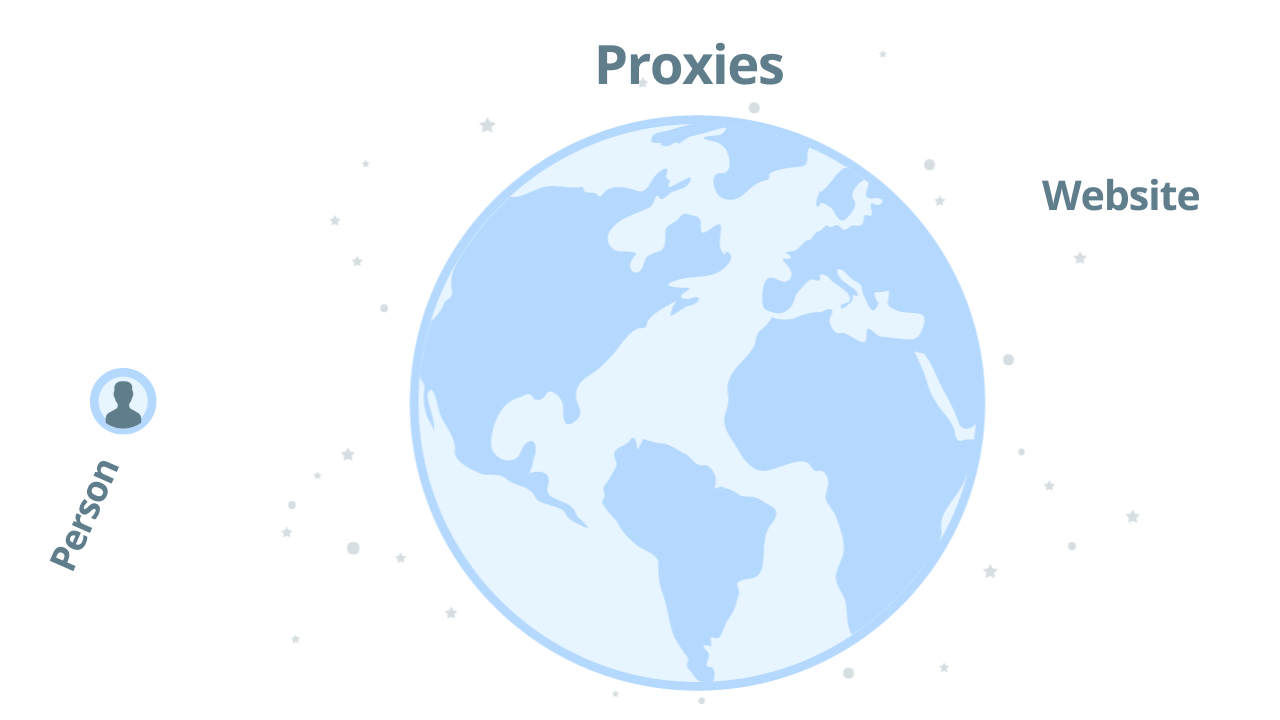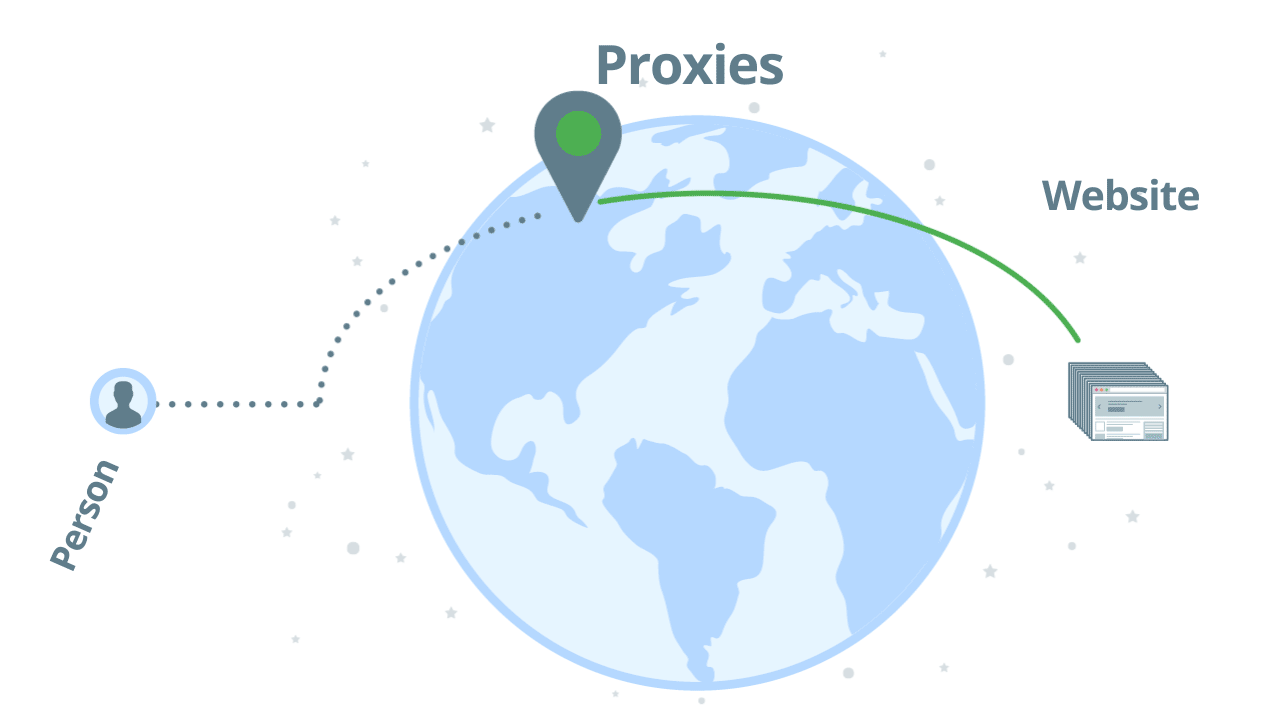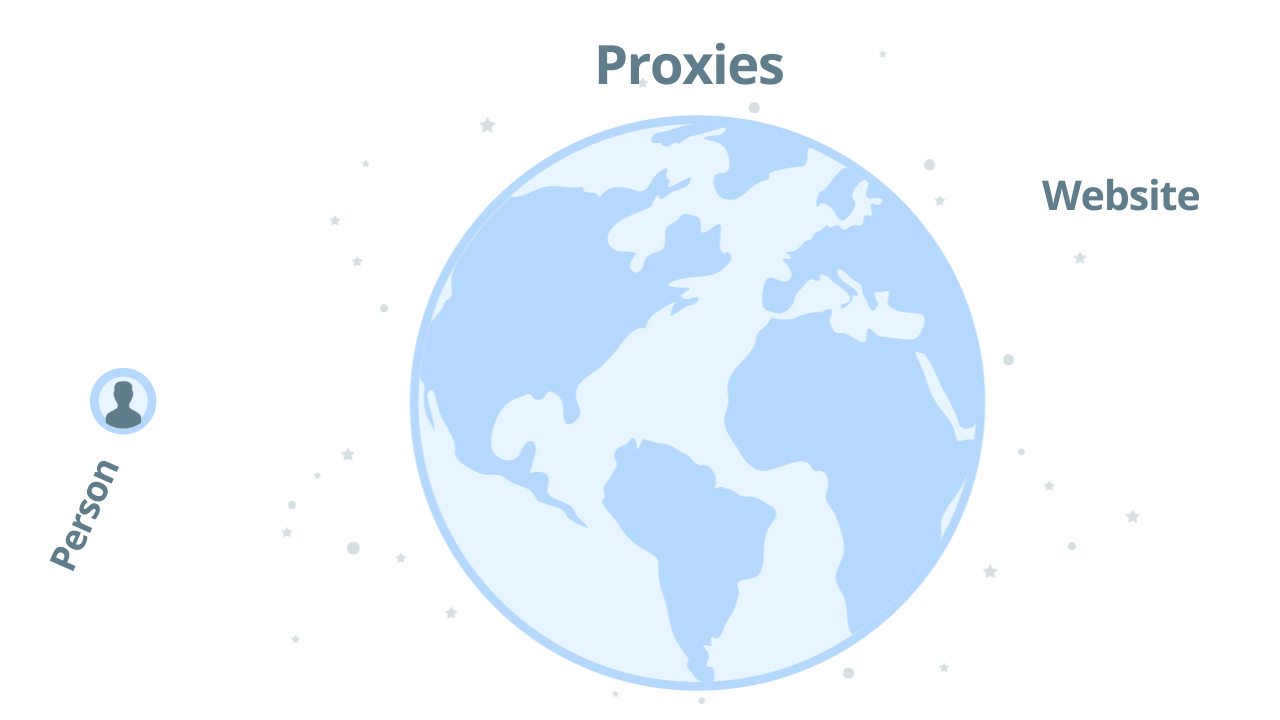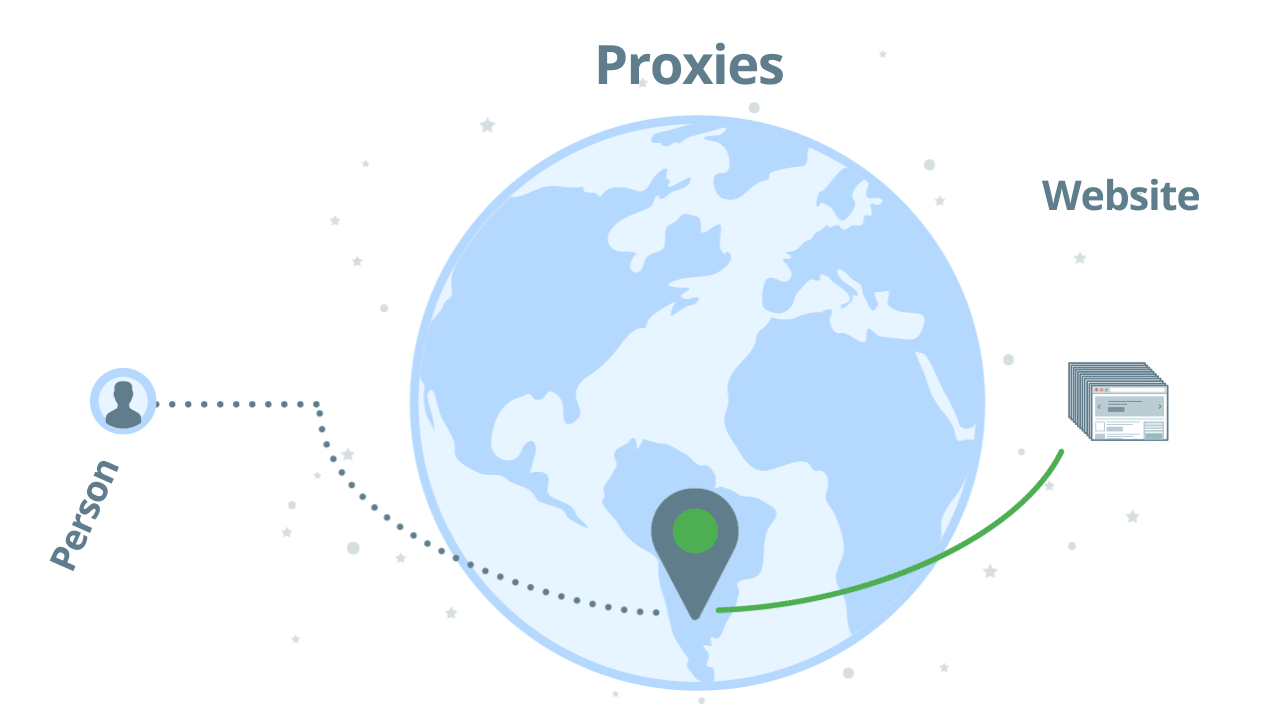
Using regular proxies is not a scalable solution unless you implement your proxy management solution. Main challenges of proxy management: identify bans, rotate proxies, user agent management, add delays, and geo-targeting.
How backconnect proxies work
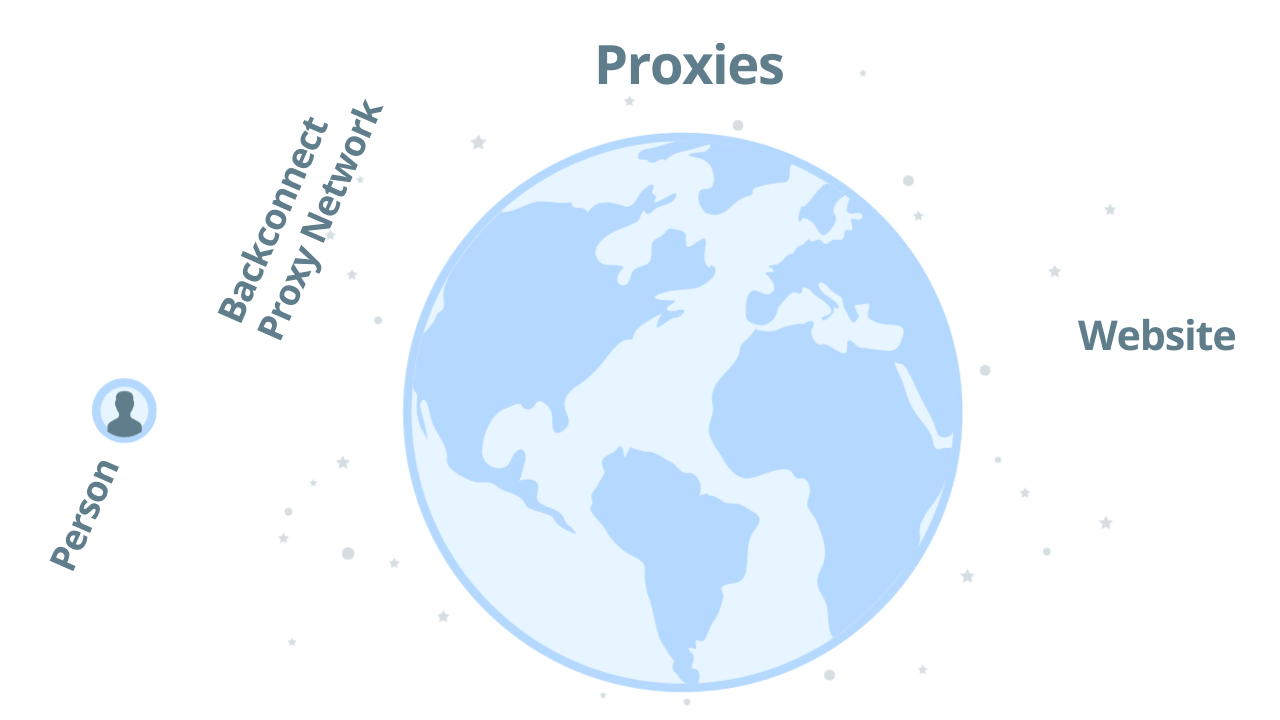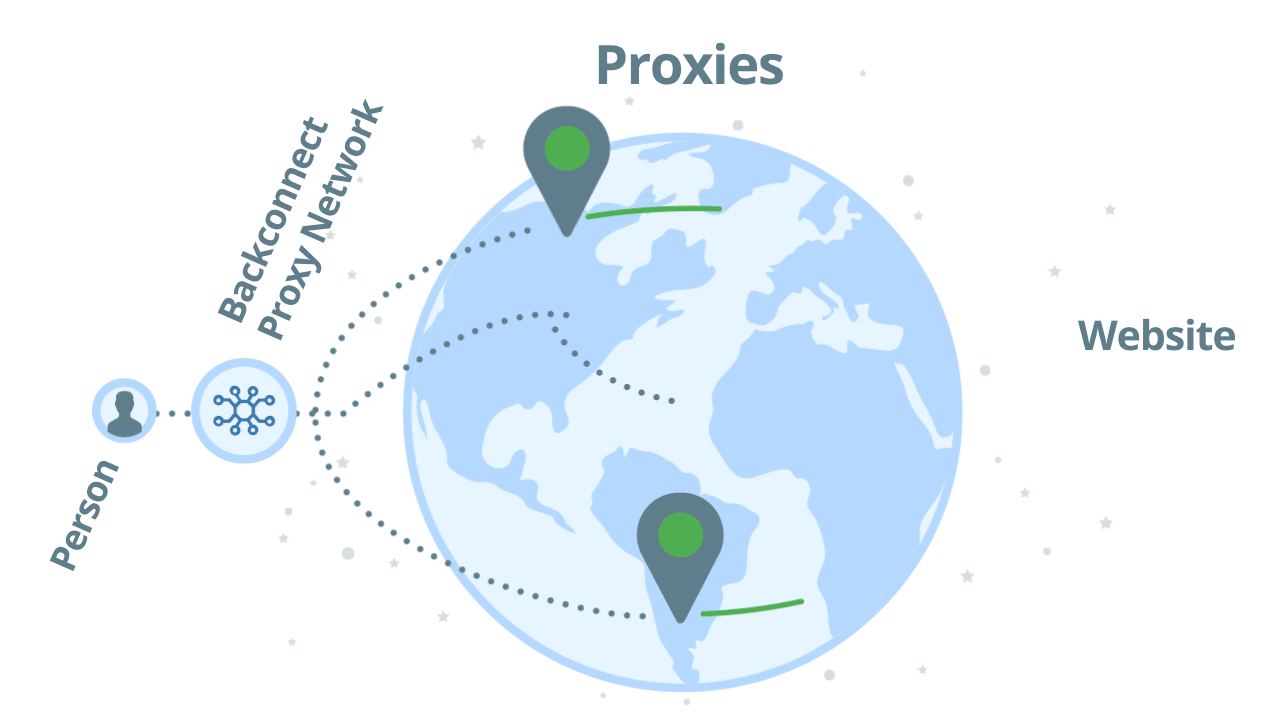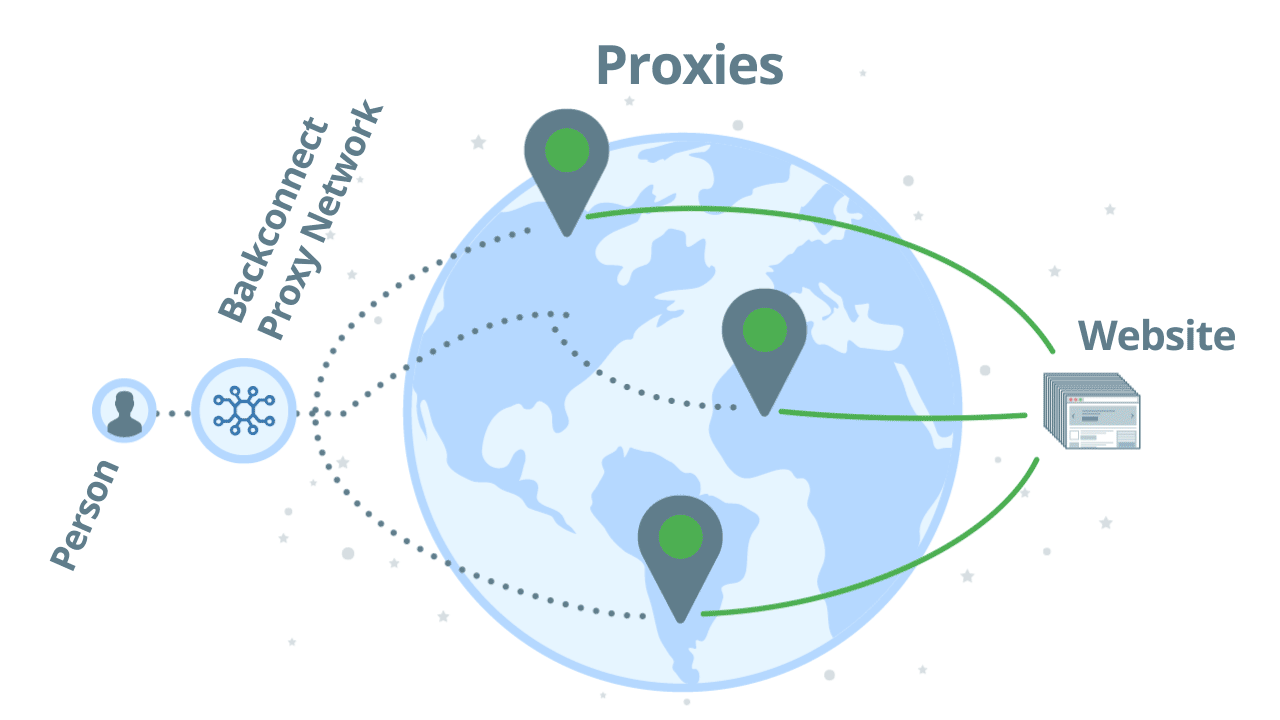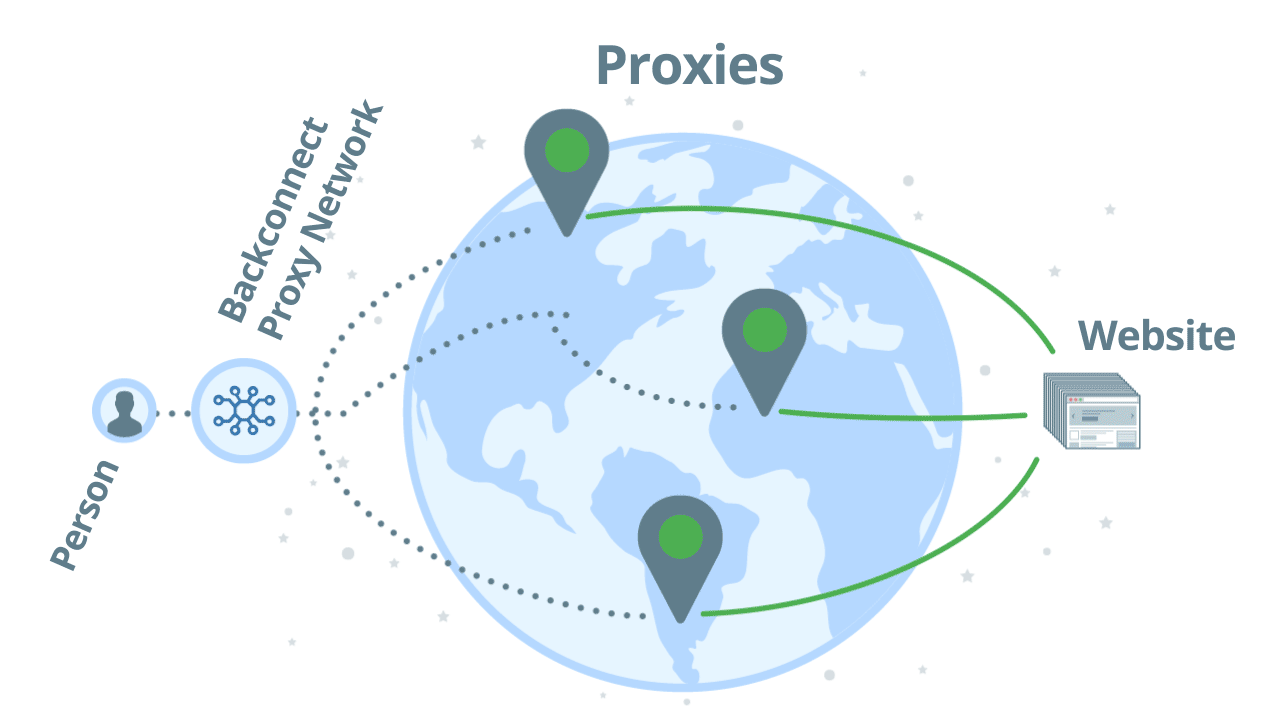
Backconnect proxies are an easy way to handle multiple requests. You can think of it as a pool of IP addresses, from the list above, plus proxy management. Unlike regular proxies where you need to send your requests through different proxies manually, with backconnect proxies you need to send all your requests through one proxy network only. Which then assigns a working IP address for you. If it gets banned you automatically get another IP address, then another, and so on. As a user, it’s hassle-free.
If you use a backconnect proxy for scraping, you don’t directly access proxies one by one. Instead, you access a pool of proxies and you will instantly get a proxy that can reach the target website with relative ease. As an example, let’s see how our backconnect proxy, Zyte Smart Proxy Manager works:
Using backconnect proxies with automatic ban detection, you can scale up your web scraping projects to millions of requests per day. As you don’t directly access the proxies, but through a network, your original IP address will be untraceable.
Features to look for when choosing a backconnect proxy provider:
- Geographically distributed
- Intelligent netloc specific proxy rotation logic
- Browser profile management
- Throttling algorithms
- Built-In session management
Be respectful
It’s also important to be respectful when crawling websites. This means, do not harm the website by sending too many requests. If necessary, limit the number of concurrent requests or wait between requests. Read our web scraping best practices guide for more information.
Why would you choose Zyte Smart Proxy Manager as your backconnect rotating proxy provider?
Performance
Having a quality proxy pool at your fingertips is already a huge advantage over regular proxies but our managed backconnect rotating proxy network has much more features to combat blocks. Features like automatic proxy rotation, geolocation, custom user agents, configurable browser profiles, and cookies. With these, you will be able to achieve your desired requests per minute (RPM) or throughput with a minimum of fuss.
Cost
Zyte Smart Proxy Manager's quality proxy pool combined with intelligent proxy rotation and automatic ban avoidance capabilities allows you to leverage datacenter proxies to the greatest possible degree. Using residential proxies optimally, therefore keeping the costs down.

If you want to experience what Zyte Smart Proxy Manager is capable of, TRY IT FOR FREE!

